9536. Sum of matrices
Given two matrices A and B.
Find their sum C = A + B.
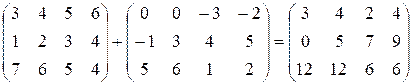
Input. The first line contains the dimensions of the
matrices – two integers n and m (1 ≤ n,
m ≤ 100).
Then follow n lines with m integers
each, describing matrix A. After that comes an empty line, followed by matrix B
given in the same format.
Output. Print matrix Ñ: n lines
with m integers.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
3 4 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 7 6 5 4 0 0 -3 -2 -1 3 4 5 5 6 1 2 |
3 4 2 4 0 5 7 9 12 12 6 6 |
SOLUTION
algebra
Algorithm analysis
Given matrices À and Â, compute
their sum – the matrix Ñ, where
Ñij = Aij + Bij
Algorithm implementation
Declare the matrices a, b
and c.
#define MAX 101
int a[MAX][MAX], b[MAX][MAX], c[MAX][MAX];
Read the input data – matrices À and Â.
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
scanf("%d", &b[i][j]);
Compute the sum of the matrices: C = A + B.
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
c[i][j] = a[i][j] + b[i][j];
Print the resulting matrix.
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < m;
j++)
printf("%d ", c[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
Algorithm implementation – double pointer
Declare
the matrices a, b and c as double pointers.
int **a, **b, **c;
The function Read reads the matrix matr.
void Read(int **&matr,
int n, int m)
{
matr = new int* [n];
for (i
= 0; i < n; i++)
{
matr[i] = new int[m];
for (j
= 0; j < m; j++)
scanf("%d", &matr[i][j]);
}
}
The function Sum
computes the sum of the matrices A + B and stores it in matrix C.
void Sum(int **a,
int **b,
int **&c,
int n, int m)
{
c = new int* [n];
for (i
= 0; i < n; i++)
{
c[i] = new int[m];
for (j
= 0; j < m; j++)
c[i][j] = a[i][j] + b[i][j];
}
}
The function Print prints matrix A.
void Print(int **a)
{
for (i
= 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (j
= 0; j < m; j++)
printf("%d ", a[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
The main part of the program. Read the dimensions of the matrices n and m.
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
Read the matrices a and b.
Read(a,
n, m);
Read(b,
n, m);
Compute the sum of the matrices C = A + B.
Sum(a,
b, c, n, m);
Print the resulting matrix.
Print(c);