9628. Frog
There are n stones, numbered from 1 to n. For each i (1 ≤ i ≤ n), the height of the
i-th stone is hi. The frog initially sits on stone 1. It repeats
the following action several times to reach stone n: if the frog is on stone i,
it can jump either to stone i + 1 or
to stone i + 2. The cost of
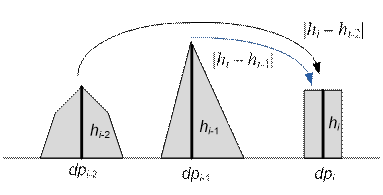
moving from the i-th to the j-th stone is |hi − hj
|.
Find the minimum
cost of moving the frog to stone n.
Input. The first line contains the number of stones
n (2 ≤ n ≤ 105). The second line contains integers h1, h2, ..., hn (1
≤ hi ≤ 104).
Output. Print the minimum cost of moving the frog to
stone n.
|
Sample
input |
Sample
output |
|
4 10 30 40 20 |
30 |
SOLUTION
dynamic programming
Algorithm analysis
Let dp[i] be the minimum cost of moving the
frog to stone i. Then:
·
dp[1] = 0 (no need to move anywhere),
·
dp[2] = | h2 − h1 |;
The frog can jump to the i (i
≥ 3)-th stone:
·
either from the (i – 1)-th stone with a cost of |hi – hi-1|;
·
or from the (i – 2)-th stone with a cost of |hi – hi-2|;
Hence
dp[i] = min( dp[i – 1] +
|hi – hi-1| , dp[i – 2] +
|hi – hi-2| )
Example
For the given
example, the frog’s path with
a cost of 20 + 10 = 30 looks like:
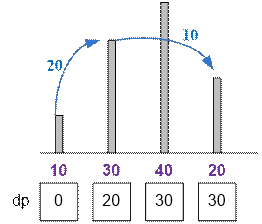
·
dp[1] = 0;
·
dp[2] = | h2 − h1 | = | 30 − 10
| = 20;
·
dp[3] = min( dp[2] + |h3 – h2| , dp[1] + |h3 – h1| ) =
min( 20 + | 40 − 30
| , 0 + | 40 − 10 | ) = min(30, 30) =
30;
·
dp[4] = min( dp[3] + |h4 – h3| , dp[2] + |h4 – h2| ) =
min( 30 + | 20 − 40
| , 20 + | 20 − 30
| ) = min(50, 30) =
30;
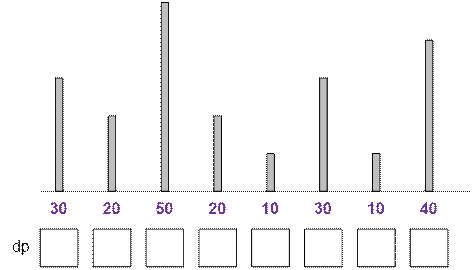
Exercise
Fill the dp array for the
following example:
Algorithm implementation
Declare the
arrays.
#define MAX 100001
int h[MAX], dp[MAX];
Read the
input data. Store the heights of the stones in the array h.
scanf("%d", &n);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d",
&h[i]);
Initialize the
values of dp[1] and dp[2].
dp[1] = 0;
dp[2] = abs(h[2] - h[1]);
Compute the
values of dp[i] (3 ≤ i
≤ n).
for (i = 3; i <= n; i++)
{
a = dp[i -
1] + abs(h[i] - h[i - 1]);
b = dp[i -
2] + abs(h[i] - h[i - 2]);
dp[i] =
min(a, b);
}
Print the
answer.
printf("%d\n",
dp[n]);
Java implementation
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
static int h[], dp[];
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
h = new int[n+1];
dp = new int[n+1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
h[i] = con.nextInt();
dp[1] = 0; dp[2] = Math.abs(h[2] - h[1]);
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
{
int a = dp[i - 1] + Math.abs(h[i] - h[i - 1]);
int b = dp[i - 2] + Math.abs(h[i] - h[i - 2]);
dp[i] = Math.min(a, b);
}
System.out.println(dp[n]);
con.close();
}
}
Python implementation
Read the
input data. Store the heights of the stones in the list h.
n = int(input())
h = list(map(int, input().split()))
Initialize
the list dp and assign values to dp[1] and dp[2].
dp = [0] * (n
+ 1)
dp[1] = 0
dp[2] = abs(h[1] - h[0])
Compute the
values of dp[i] (3 ≤ i
≤ n).
for i in range(3, n + 1):
a = dp[i - 1] + abs(h[i - 1] - h[i
- 2])
b = dp[i - 2] + abs(h[i - 1] - h[i
- 3])
dp[i] = min(a, b)
Print the
answer.
print(dp[n])