9631. Competition of sequences
Ziya will take part in the
sequence competition tomorrow. The number x ≥ 0 is called the top
of some sequence if the sequence 1, 2, 3, ..., x – 1, x, x
– 1, ..., 3, 2, 1 is a subsequence of this sequence. The strength of each
sequence is considered to be its largest vertex.
Tomorrow all students will
go to the competition and the winner of the strongest sequence will be the
winner. Zia has the sequence a1, a2, a3, ..., an. He wants to take over
the competition scoring system and remove sequences from it with more force
than himself. However, Zia does not know the power of his own consistency, but
really wants to win. Help him calculate the strength of his own sequence.
Input. The
first line contains the number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) of numbers in Zia's sequence. The next line contains n
integers ai (1 ≤
ai ≤ 105) – the elements of the sequence.
Output. Print
one number – the strength of the given sequence.
|
Sample
input 1 |
Sample
output 1 |
|
2 2 10 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
Sample
input 2 |
Sample
output 2 |
|
3 1 2 3 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
Sample
input 3 |
Sample
output 3 |
|
5 1 10 2 3 1 |
2 |
SOLUTION
two pointers
Algorithm analysis
Let v
be the input array of numbers. Initialize the pointers i = 0 at the beginning of the array and j = n – 1 at the end of the array. We will count the
strength of the sequence in the variable k. Initially, set k = 1.
While the
pointers i and j do not
meet, perform the following actions:
·
Move
the pointer i
one position to the right if it does not point to the number k.
·
Move
the pointer j one position to the left if it does not point to the
number k.
·
If
both pointers point to the number k, increase k
by one and move each pointer one position in the corresponding direction.
After the
algorithm completes, the answer will be the value k – 1.
Example
Consider the second test.
Initialize the pointers. Move the pointer i to the right and the
pointer j to the left until they both point to the number 1.

Move the
pointer i to the right and the
pointer j to the left until they
both point to the number 2.
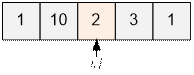
The
pointers meet, we stop the algorithm. The answer will be the value k = 2.
Algorithm realization
Read the input data.
scanf("%d", &n);
v.resize(n);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &v[i]);
Set the pointers to the start and end of the array v.
int i = 0, j = v.size() - 1;
In the variable k, we count the strength of the
sequence.
k = 1;
while (i <= j)
{
Move the pointer i to the
right until it encounters the number k.
if (v[i] != k)
i++;
Move the pointer j to the left
until it encounters the number k.
if (v[j] != k)
j--;
If both pointers point to the number k, then increase k
by one.
if (v[i] == k
&& v[j] == k) k++;
}
Print the answer.
printf("%d\n", k - 1);
Python realization
Read the input data.
n = int(input())
v = list(map(int, input().split()))
Set the pointers to the start and end of the list v.
i, j = 0, len(v) – 1
In the variable k, we count the strength of the
sequence.
k = 1
while i <= j:
Move the pointer i to the
right until it encounters the number k.
if v[i] != k:
i += 1
Move the pointer j to the left
until it encounters the number k.
if v[j] != k:
j -= 1
If both pointers point to the number k, then increase k
by one.
if v[i] == k and v[j] == k:
k += 1
Print the answer.
print(k - 1)