61. Rotate List
Given a list, rotate the
list to the right by k places, where k is non-negative.
For example, given 1
→ 2 → 3 → 4 → 5 → NULL and k = 2,
return 4 → 5 →
1 → 2 → 3 → NULL.
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head,
int k) {
}
};
SOLUTION
Algorithm analysys
If the list is empty or k = 0, return head.
Find the length len of the list. If k is
divisible by len, then
after rotation the list will take the original form. In
this case return head, doing nothing
with the list.
The value k can
be greater than len, so
its enough to rotate a list k % len positions right.
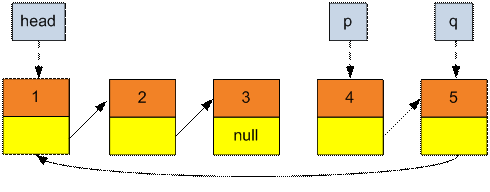
Find the head of the new list, assign pointer q to it. Assign pointer p to ListNode before q.
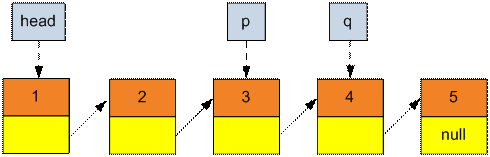
Set p → next = NULL.
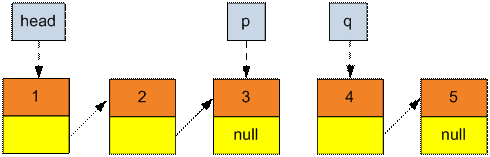
Make an assignment p = q.
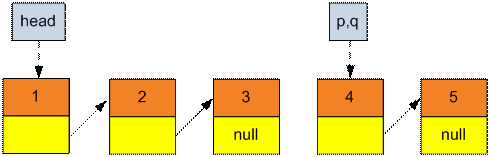
Move the pointer q to
the end of the list till q → next will
not become
NULL).
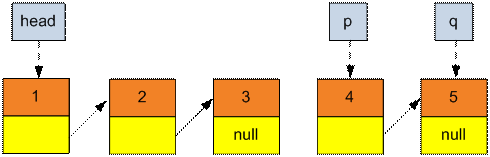
Assign q → next the
value of head. The head of the new list is p.
Algorithm realization
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode*
rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k)
{
if ((head == NULL) || (k == 0)) return head;
ListNode *p = head;
int len = 0;
while(p != NULL)
{
p = p->next;
len++;
}
if (k % len == 0) return
head;
k = k % len;
p = head;
for(int i = 0; i <
len - k - 1; i++)
p = p->next;
ListNode *q =
p->next;
p->next = NULL;
p = q;
while(q->next != NULL)
q = q->next;
q->next = head;
return p;
}
};